Post-fracture physiotherapy treatment is crucial as it emphasizes early mobilization, gait training, and other treatment modalities to maintain or restore potential impairments.
Physiotherapy intervention has indeed had a positive impact on gaining more confidence. A fracture is no doubt often written as in medical shorthand, i.e., the hash symbol.
Most commonly, fractures do occur in the setting of a normal bone with acute, overwhelming force, usually in the setting of trauma. Fractures can also occur in other settings as well.
Initially, the entire skeleton can be weak due to metabolic (e.g., osteoporosis) or less frequently genetic abnormalities (e.g., osteogenesis imperfecta) and be prone to fractures from forces that are insufficient to cause fractures in normal bones. These are, of course, known as insufficiency fractures.
Secondly, the protracted chronic application of abnormal stresses (e.g., running) can rather result in the accumulation of micro-fractures faster than the body can heal, resulting in macroscopic failure. These are rather termed fatigue fractures.
Together, insufficiency as well as fatigue fractures are often grouped as stress fractures.
Thirdly, the bone may have a lesion that does focally weaken it (e.g., metastasis, bone cyst, etc.). These are referred to as pathological fractures.
Rarely is the term ‘fracture’ used for non-osseous or chondral structures (e.g., penile fracture), although if unqualified, it is known as a bony fracture.
Although several eponymous fractures do exist and the relevant particulars of a fracture tend to depend on its specific location, usually fractures are described consistently.
Importance of post-fracture physiotherapy treatment
The physiotherapist’s role is to identify the cause of the problem and also to select the appropriate procedure to alleviate or eliminate the cause of the loss of movement.
Early treatment includes:
- A physical therapist can instruct the client on how to walk with an assistive device, such as a cane or crutches. This includes how to use the device to walk up and down stairs or even to get into and out of a car. Learning a new skill does take practice, so be sure to allow clients to practice making use of one’s device while having it.
- After a lower extremity fracture there can limit the amount of weight a client can put on the leg can be limited. Helping the client understand weight-bearing restrictions and also teaching how to move about while still maintaining these sorts of restrictions.
- If the fracture is in the arm, then the physical therapist can teach how to apply and remove the sling.
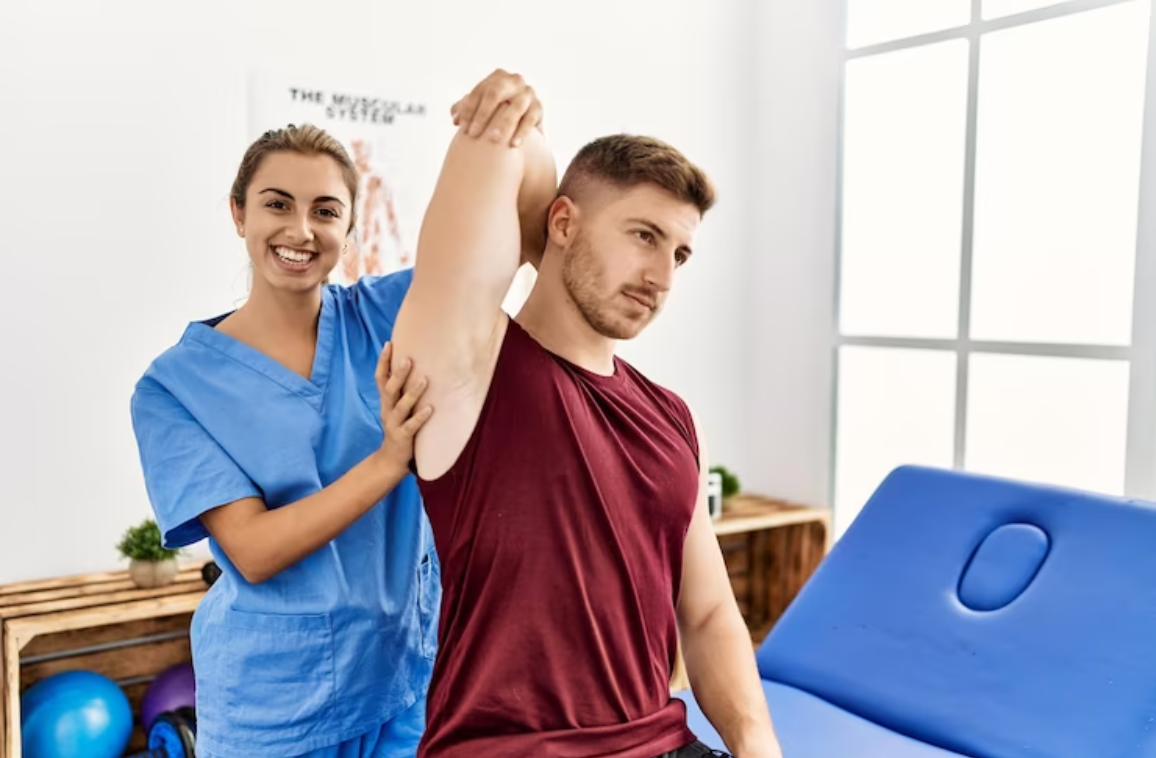

Assessing the patient is indeed necessary. Information about allergies, past medical history, past surgical history, family history, and social history (living arrangements, social conditions, employment, medication) can turn out to be a review of systems.
- Objective: All information obtained through observation or even testing, e.g., range of joint movement, and muscle strength, is taken into consideration.
- Analysis: a listing of problems that are based on what the person knows from a review of subjective and objective data.
- Plan: This refers to the plan of treatment.
By making use of specific exercises, the aim is to reduce any kind of swelling, regain full muscle power and joint movement, and bring back full function. The sort of treatment will much depend on the problems identified during the initial assessment, but can include a mixture of the following:
- Soft tissue massage, particularly to manage edema and swelling.
- Scar management in case the patient had surgery to fix the fracture.
- Ice therapy.
- Stretching exercises to regain joint range of movement.
- Joint manual therapy and mobilizations to assist in regaining joint mobility.
- Structured and progressive strengthening regime.
- Balance and control work, as well as gait (walking) re-education where appropriate.
- Taping to support the injured area or help with swelling management.
- Return to sport preparatory work and then advice where required.
Conclusion
Patients demonstrate a high level of satisfaction with the improvement in their condition after rehabilitation therapies and lead fully active and independent lives. Post-fracture physiotherapy treatment is useful.