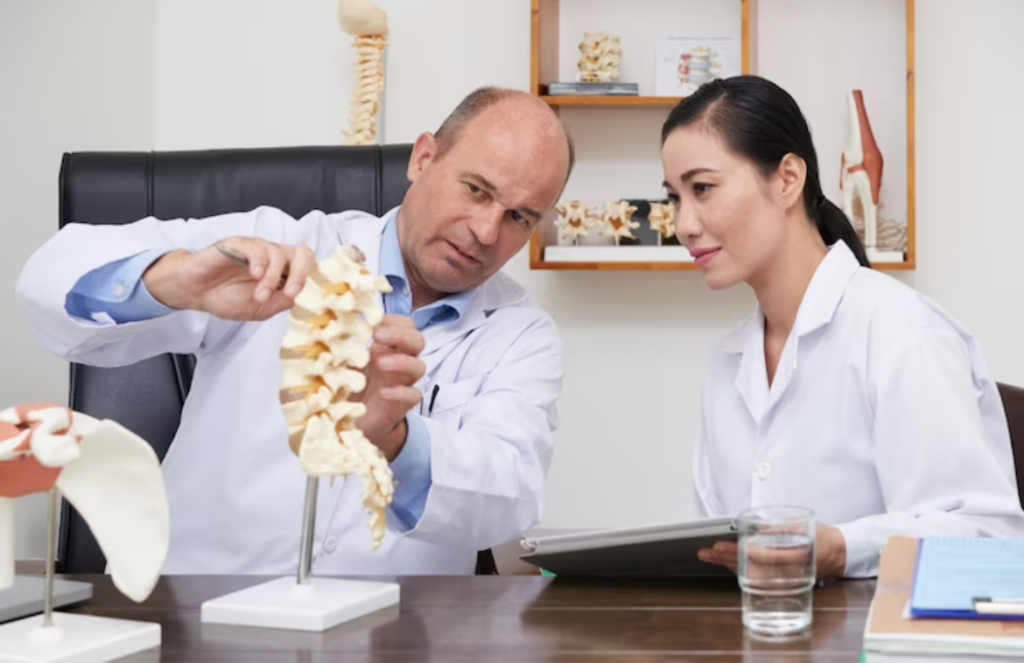
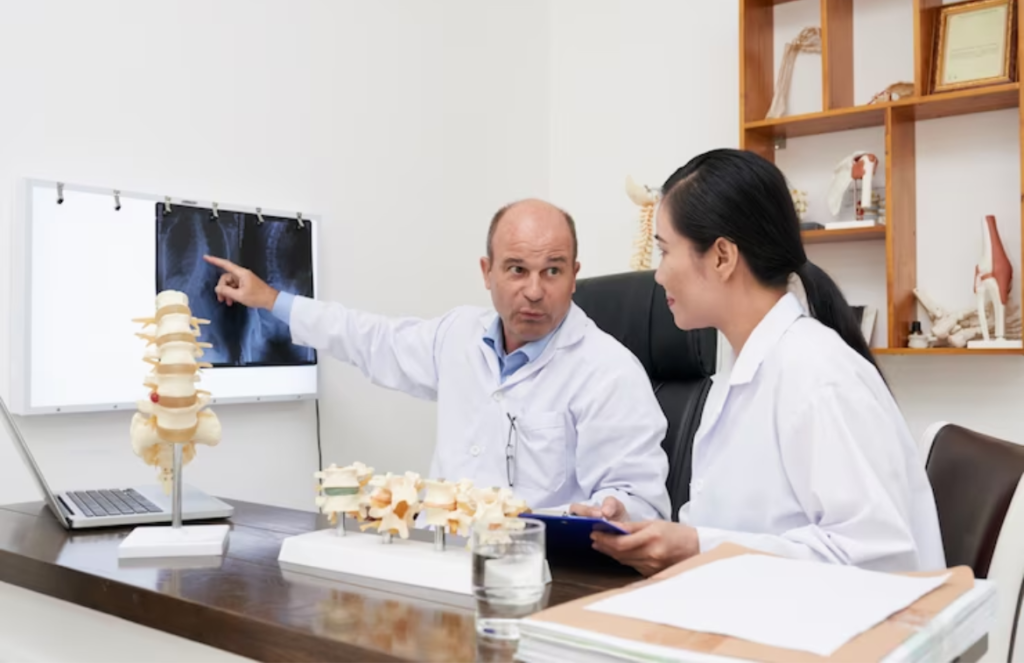
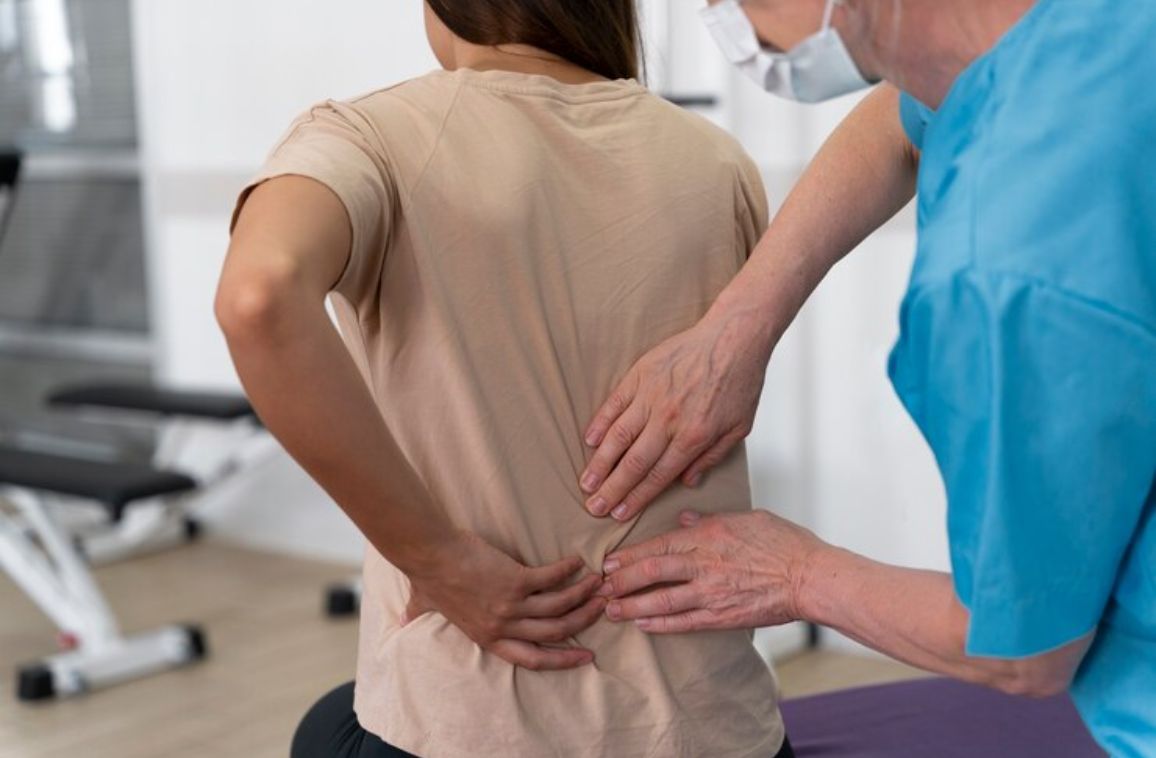
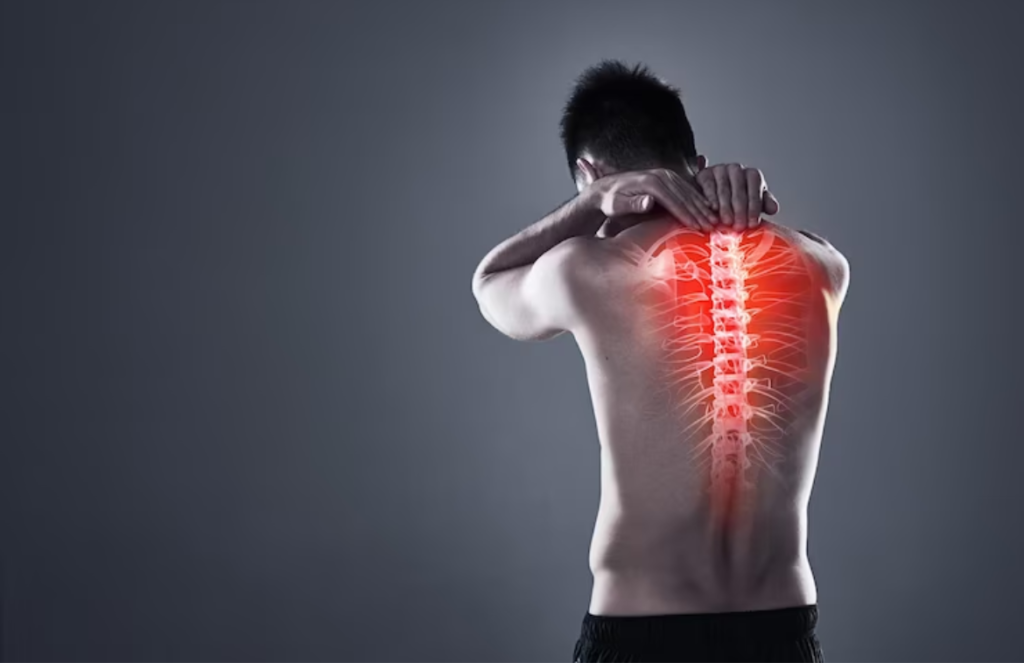
Spinal problems symptoms refer to diseases or injuries that affect the spine, like spinal stenosis. They do cause symptoms that include lower back pain, numbness, tingling sensations, and much discomfort.
There are several types of spinal conditions that can cause pain and discomfort, and these conditions can result from:
- Genetics.
- Aging.
- Accidents.
- Injuries.
Spinal conditions can indeed cause back pain, which happens to be one of the most common medical problems. A spinal cord injury does involve damage to any part of the spinal cord. It can also include damage to one’s nerves at the end of the spinal cord, known as the cauda equina. The spinal cord does send and receives signals between the brain and the rest of one’s body. A spinal cord injury often causes permanent changes in strength, feeling, and other body functions below the site of the injury.
People who have had a spinal cord injury can also experience mental, emotional, and social side effects.
Many scientists are indeed very optimistic and feel that advances in research will someday make the repair of spinal cord injuries possible.
Spinal condition definition
A spinal condition is indeed a disease or injury that mostly affects the back or spine. The spine consists of five regions:
- Cervical spine.
- Thoracic spine.
- Sacrum.
- Lumbar spine.
- Coccyx.
Most people are born with 33 vertebral bones, but few bones in the coccyx fuse throughout childhood. This implies that adults have 24 vertebrae.
Spinal conditions can no doubt cause discomfort, pain, and mobility issues.
Specialists, like orthopedic doctors and surgeons, concentrate on helping people with spinal conditions.
Chiropractors can also help with back problems, but they are not medical doctors and cannot diagnose conditions or even provide prescription treatments.
Common symptoms
The symptoms of a spinal condition depend greatly on the diagnosis. However, spinal problems can cause one or more of the following symptoms:
- Back as well as neck pain.
- Numbness.
- Tingling sensation.
- Pain in the legs, arms, or even both.
- If all sense of feeling and all ability to control one’s movement is lost below the spinal cord injury, the injury is known as complete.
- If little feeling and control of movement remain below the affected area, the injury is known as incomplete. Loss of feeling and control of movement is referred to as paralysis. Your healthcare team performs a series of tests to determine the neurological level and completeness of your injury.
Spinal problem symptoms:
- Loss of movement.
- Loss of or even a change in sensation. This includes a change in the ability to even feel heat, cold, and touch.
- Loss of bowel or even bladder control.
- Exaggerated reflex activities or even spasms.
- Changes in sexual function, sexual sensitivity, and fertility.
- Pain, or perhaps an intense stinging sensation, is caused by damage to the nerve fibers in one’s spinal cord.
- Trouble breathing, coughing, or rather clearing secretions from the lungs.
Emergency symptoms
Emergency symptoms of a spinal cord injury after an accident include:
- Extreme back pain or even pressure in the neck, head, or back.
- Weakness, incoordination, or loss of control in any part of one’s body.
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of feeling in the hands, fingers, feet, or one’s toes.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Trouble with balance and walking.
- Trouble breathing after an injury.
- twisted neck or back.
Possible causes and risk factors
The causes and risk factors for a spinal problem include:
- Accidents or falls.
- Violence.
- Genetics.
- Being overweight or obese.
- Poor posture.
- Nutrition and lifestyle habits, such as smoking.
- Age-related changes, e.g., spinal degeneration and reduced activity.
Conclusion
Several diseases affect the spine, and they also affect the bones, nerves, or perhaps surrounding tissues. Several causes of back pain are treatable, but few are lifelong conditions.