Orthopedic health has to be ensured for overall well-being. Nutrition in orthopedic health cannot be overlooked and medical professionals do give it much importance.
Good nutrition does indeed play an important role in recovery from planned orthopedics surgery or even traumatic injury. In the orthopedic patient, poor nutrition can rather delay wound healing as well as fracture repair, increase the risk of infection, decrease muscle strength, lead to the development of constipation, and also ultimately delay recovery.
Fractures are rather quite common, especially among the elderly. Yet, they can increase in prevalence at younger ages too if bone health is not good. This can happen as a result of bad nutrition.
Insufficient intake of certain types of vitamins, particularly A and D, as well as other nutrients, such as calcium, may rather affect bone health or even the time as well as the degree of bone healing in case of fracture. The importance of different nutrients, both dietary and those found in food supplements, is discussed concerning bone health as well as fracture healing.
The role of nutrition in bone health is no doubt important. Adopting a balanced diet, rich in nutrients, minerals, as well as vitamins, can contribute significantly to bone health. Proper nutrition is indeed an essential parameter of skeletal health, participating in both the prevention as well as treatment of bone diseases. A chronic vegetarian diet can lead to problems of osteoporosis. Heredity, impaired hormonal function, pregnancy as well as lactation, nutrition, exercise, and also various diseases (like bronchial asthma, anorexia nervosa, as well as corticosteroids) affect the attainment of peak bone density.
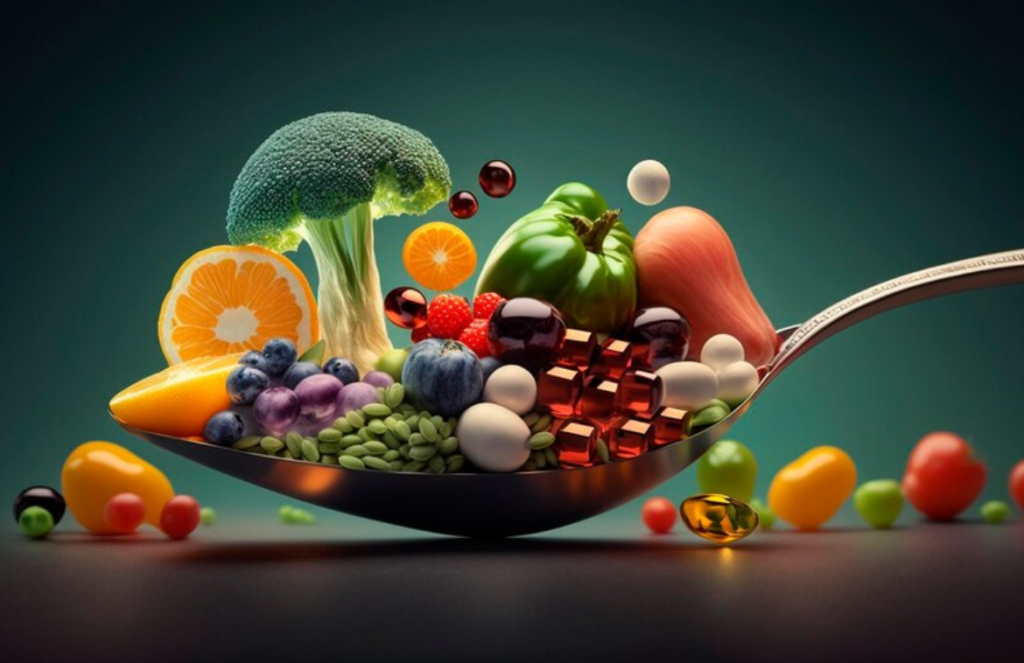

Osteoporosis can easily no doubt lead to fractures. A patient suffering from osteoporosis need to have calculated the anticipated fracture risk, or this risk is enhanced. A good nutritional program can rather prevent osteoporosis and also regulate other nutrient deficiency problems and, consequently, prevent fractures.
Mechanisms and Effects on Bone
Regulation of calcium homeostasis as well as bone metabolism does occur via the action of vitamin D on its target tissues including the intestine, kidneys, and also bone. Vitamin D can act at genomic as well as non-genomic levels.
Vitamin D Metabolism and Toxicity
Vitamin-D is considered to initially generate in the skin from the non-enzymatic conversion of pro-vitamin D3. Dietary intake of vitamin D is indeed relatively limited, since few foods except a few types of fish, contain sizable amounts.
The importance of a nutritional assessment and the subsequent interventions along with the role of hydration and dehydration are o much significance in bone health. Six major components to be considered essential in the human diet are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals as well as water. Carbohydrates, proteins as well as fat are known as macronutrients and are essential in large quantities as compared to micronutrients. The orthopedic patient is really at risk of malnutrition if their intake of nutrients is impacted by co-morbidities, surgery, or underlying problems that do affect appetite or absorption of food.
Conclusion
It is quite evident that the role of nutrition in bone health is quite important. Adopting a balanced diet, rich in nutrients, minerals, as well as vitamins, can indeed contribute much to bone health. Proper nutrition is an essential parameter of skeletal health, thus playing a major role in both the prevention as well as treatment of bone diseases.
A chronic vegetarian diet can lead to problems of osteoporosis. Heredity-impaired hormonal function, pregnancy as well as lactation, nutrition, exercise, and also various diseases (such as bronchial asthma, anorexia nervosa, and corticosteroids) do affect the attainment of peak bone density. Nutrition in orthopedic health is an important component of bone health.